Carotid (carotid artery) Angiography
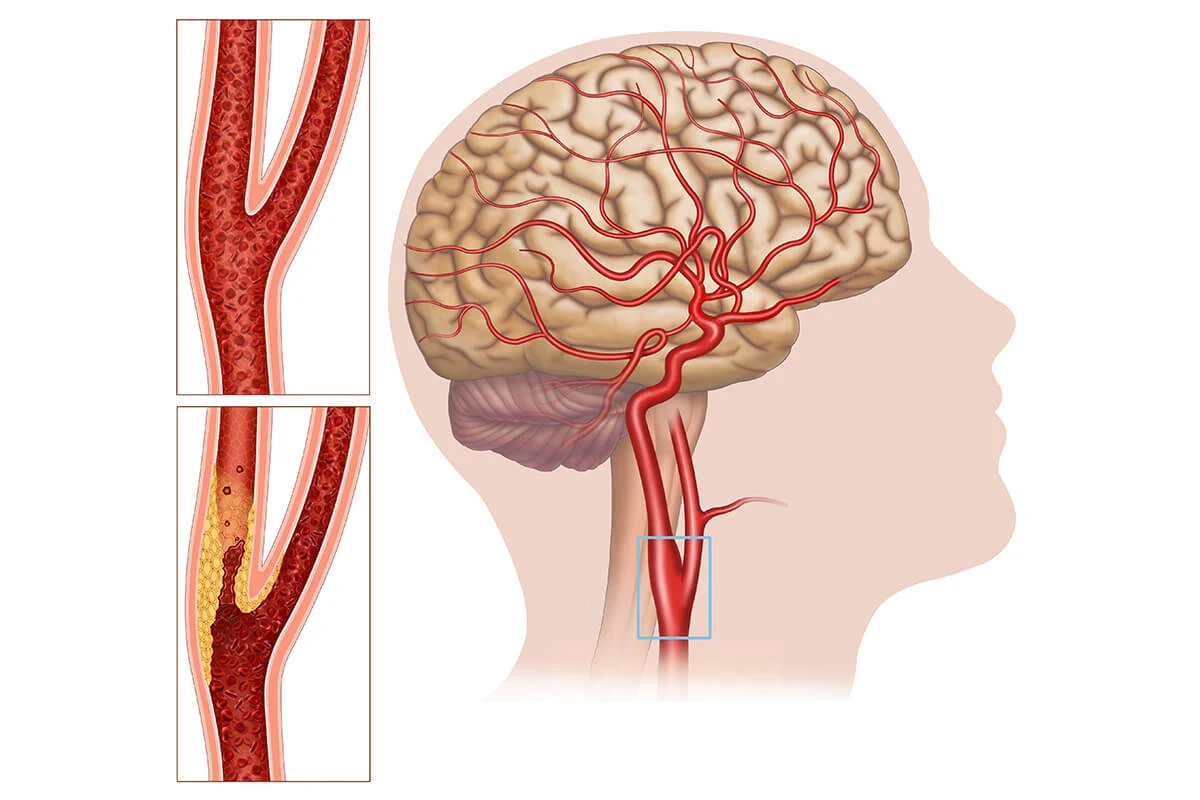
We have carotid arteries (commonly known as the “carotid artery”) on both sides of our neck. Carotid artery disease can lead to stroke or cerebrovascular attacks, making it a potentially serious condition.
A stroke occurs when the blood flow to the brain is interrupted due to the blockage of the artery or the formation of a clot, often due to atherosclerosis. If the blood flow to the brain is interrupted for more than a few minutes, brain cells begin to die. Stroke can result in brain damage, paralysis, long-term disabilities, and even death. Carotid artery disease may not show symptoms until there is severe narrowing or complete blockage in the carotid arteries. In some individuals, stroke can be the first sign of carotid artery disease. Carotid artery disease is a major cause of stroke, along with heart problems and brain hemorrhages.
The causes of carotid artery blockage and stroke include:
– Use of tobacco and tobacco products
– High levels of fat and cholesterol in the blood
– High blood pressure
– Advanced age and male gender
– Metabolic syndrome
– Lack of physical activity
– Family history of vascular stiffness
– Insulin resistance or high blood sugar levels due to diabetes play a significant role.
Individuals at risk for carotid artery blockage also form a high-risk group for the development of coronary artery disease and heart disease, as they have atherosclerosis developing throughout the body.
Having these risk factors does not necessarily mean that you will develop carotid artery disease. However, if you have one or more of these factors, it is essential to take the necessary precautions to prevent the development of the disease.
Carotid artery disease may not cause symptoms and signs until the carotid arteries are significantly narrowed or completely blocked. The main symptoms that can be observed include the detection of a murmur due to narrowing in the neck during a careful examination, as well as transient ischemic attacks, which are temporary stroke-like symptoms that resolve within 24 hours. Stroke can also be a notable manifestation.
- Various degrees of weakness and/or numbness, including the face, on one side of the body
- Difficulty in speech and comprehension, sudden loss of vision or decreased vision in one or both eyes
- Dizziness or loss of balance
- Sudden and severe headache without any apparent cause
- These symptoms, sometimes of very short duration, can be a sign of a severe impending stroke. It is essential to seek urgent medical attention.
- Otherwise, the development of a stroke can lead to permanent brain damage, paralysis, loss of various bodily functions, and even death.
For a comprehensive examination and diagnosis of the carotid artery, various diagnostic tools are used, including carotid Doppler ultrasound, MR angiography, CT angiography, and carotid angiography.
In the treatment of carotid artery disease, lifestyle and dietary changes, along with the use of anticoagulants and cholesterol-lowering medications, constitute the primary medication therapy. Radiological and surgical interventions are also employed as part of the treatment.
With lifestyle changes, we can prevent the development of carotid artery disease and/or prevent its progression. Adopting a healthy diet and maintaining an ideal weight can help keep your cholesterol levels within the appropriate limits and prevent the development of high blood pressure. Increasing physical activity helps maintain an ideal weight and raises the level of good cholesterol (HDL).
Avoiding the use of tobacco products is of critical importance not only for our overall health but also for cardiovascular health.
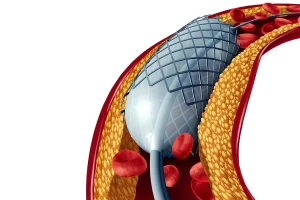
In the non-pharmacological treatment of carotid artery disease, the aim is to mechanically eliminate the narrowing in the affected area through surgical or interventional angiography techniques. The appropriate treatment method for the patient is determined based on factors such as the patient’s age, overall health status, existing risk factors, and the degree of narrowing.
Carotid endarterectomy is performed under local (regional) or general anesthesia. The surgical procedure is carried out through an incision made in the neck on the side of the patient’s affected carotid artery. The plaque causing the narrowing is removed by opening the carotid artery at the site of the stenosis. Most of our patients are discharged the day after the approximately 45-minute operation and return to their normal activities within one week.