Treatment of Palpitations by Burning or Freezing (Ablation)
Table of Contents
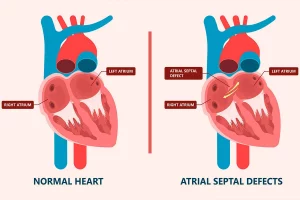
Various malfunctions can occur in the heart’s normal conduction and impulse system due to a variety of reasons. Sometimes, congenital additional pathways can create short circuits in conduction, leading to rapid heartbeats, also known as tachycardia, causing palpitations.
The diagnostic method known as Electrophysiological Study (EPS) involves the use of thin sheaths inserted into the groin artery and advanced through to the heart with the help of electrode catheters.
The electrical signals directly obtained from within the heart are evaluated using advanced computers to investigate any deviations from the norm.
What Is Catheter Ablation and How Is It Performed?
In patients with complaints of palpitations, often in the form of rapid heartbeats, the causes are explored by inducing palpitations using stimuli delivered from these electrode catheters placed inside the heart.
If the presence of short circuits is identified, the palpitations can be completely treated by delivering focal energy through radio waves.
This treatment is referred to as catheter ablation. Today, this method makes it possible to achieve permanent treatment for most cases of rapid heartbeats (tachycardia).
Risks, Recovery, and Success Rates of Ablation Treatment
Diagnostic electrophysiological examinations typically last around 30 minutes. If a therapeutic intervention is required, the procedure may take approximately 1-1.5 hours. These procedures are generally low-risk interventions.
However, like any procedure, they can have some associated complications. The likelihood of mortality is very low.
Occasionally, during therapeutic procedures (ablation), blocks may develop in the heart’s conduction system (0.5%). In about 2-3% of cases, there may be bleeding at the entry site of the blood vessel, as well as hematomas and associated swelling and pain under the skin.
However, these issues are usually not significant and tend to resolve spontaneously.
The data obtained from electrophysiological studies cannot be obtained through any other diagnostic method, making it the most valuable method for diagnosis.
The method of catheter ablation is used in the treatment of rhythm disorders that cannot be controlled with medications and/or those that could threaten life, or when patients do not want to take medication for their lifetime.
The success rate of palpitation treatment with catheter ablation varies between 70-95%. The likelihood of palpitations recurring after a successful procedure varies depending on the type of arrhythmia, typically ranging from 5-8%.
The procedure is primarily performed under local anesthesia by numbing the needle entry sites. To help you feel more comfortable during the procedure, a sedative may be administered. After the procedure, you will need to lie down without moving your legs for a few hours to prevent bleeding.